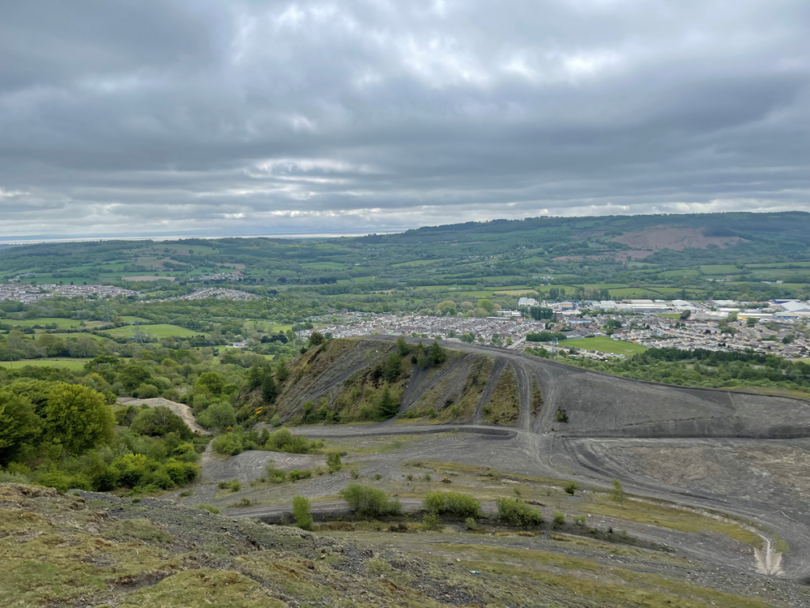
Ground engineering company Central Alliance is working with the Welsh Government on a project that will map and evaluate 83 South Wales coal tips, providing vital information on their topography and identifying any future landslip risks so that required remedial action can be scheduled.
Central Alliance Business Development Manager David Capstick said this followed phase one of the project, which was completed in 2022 and identified high-priority sites for further study.
Phase two begins in autumn and comprises three separate satellite image acquisitions. It is expected to be completed in 12 weeks after each data acquisition, with Central Alliance focusing its attention on capturing enhanced intelligence on these sites.
David said: “With all 83 sites, we will be looking at a total area in excess of 5 million square metres. Our teams, which include geographic information system (GIS) specialists and geotechnical engineers, will develop soil moisture models of the tips and adjacent areas. This data is evaluated for landslip susceptibility by using a unique, risk-based assessment tool that uses soil moisture data from L-band polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) satellite data, topography, surface drainage flow, climate conditions and landcover status. The PoISAR data set is being obtained by ASTERRA who also assisted in Phase 1 of this study.
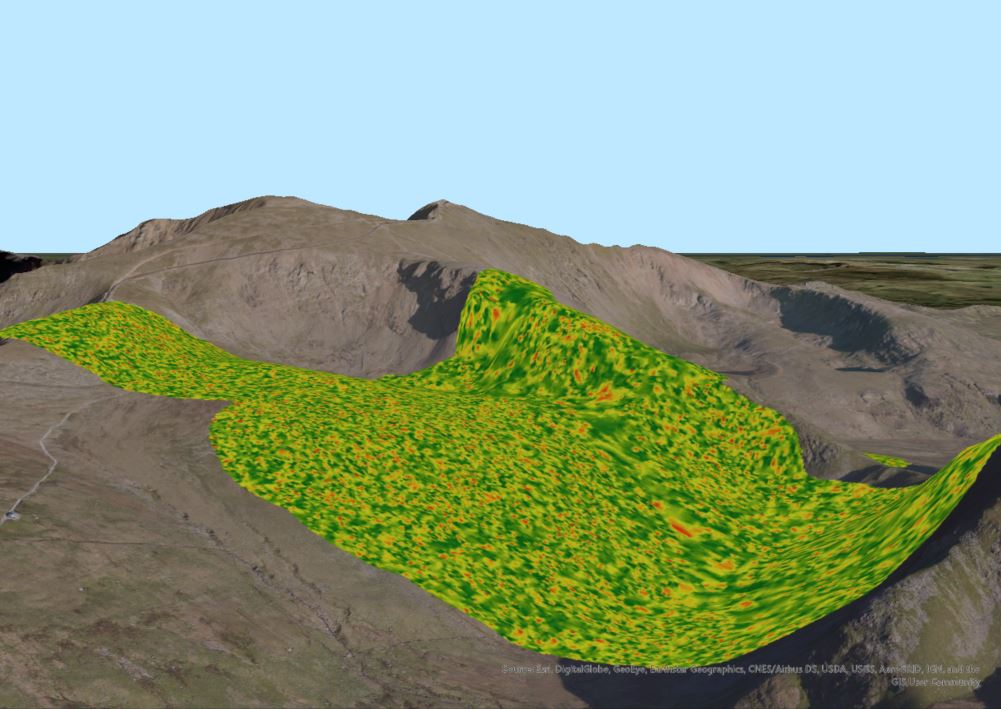
Heatmap on slope stability index values
“PolSAR refers to a mapping technique that harnesses radar images of the Earth’s surface collected from orbiting satellites. This technology is favoured because it offers an accurate picture of ground formation and deformation irrespective of weather conditions. Data from each site will be issued separately as and when complete, with a final report summarising the findings from each acquisition, issued 12 weeks after SAR image acquisition.”
He said the risk profile, derived from a comparative measure, scores spoil tips on seven different metrics in order to form a quantitative prioritisation method, which would then be displayed as a GIS analysis. This allows the team to study and assess the sites over time and to take into account different seasonal conditions. The analytics, along with the GIS outputs, enable an efficient conversion of the datasets into a 4D GIS model that presents site managers and local authorities with visual information to assist their risk management of these areas.
Dave added: “This challenge is in many ways unique to the South Wales coal fields. But the processes and principles are transferable to many climate change, environmentally driven, geotechnical challenges that affect other engineering, transport and mining projects. The ability to have an enhanced understanding of the ground conditions at specific locations provides a higher level of confidence in focusing remedial action at the most appropriate sites.”
Central Alliance offers ongoing remote access to site instrumentation during and after projects through a series of interactive dashboards to ensure that key information is accessible as it becomes available.
For more information, visit: www.rskgroup.com